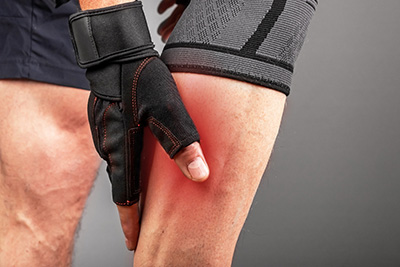
A muscle strain, also known as a pulled muscle, happens when your muscle is overstretched or torn. This is frequently caused by muscle exhaustion, overuse, or improper use. Strains can occur in any muscle, although they are most prevalent in the lower back, neck, shoulder, and thigh. These strains can be painful and restrict movement in the affected muscle area. Mild to severe strains can be treated at home successfully using ice, heat, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Severe strains or tears might require medical attention.
Muscular strains occur when the muscular fibers are torn. Muscle strains can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Home therapy is sufficient for mild to moderate strains. If any of these conditions occur, get medical attention:
A physical examination as well as imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans can assist your doctor in determining the extent of your damage. Anti-inflammatory medicines and pain relievers may be used to treat discomfort and swelling. Physical therapy may also be prescribed by your doctor to help strengthen the muscle and restore movement. In severe cases, surgery to repair the muscle may be required.
Stretching and warming up before exercise is the greatest approach to avoid muscular strains. Increased flexibility will also protect your muscles from potential injury. The more flexibility, the more room your muscle fibers have to stretch before they tear. It’s comparable to how some materials are more pliable than others. Because you’ve stretched out your favorite pair of jeans over the years, they’re quite flexible. However, you may need to wear a brand-new pair a few times before they feel comfortable. The same is true for your muscles. The more you exercise and stretch them, the more flexibility and give they have when you move.